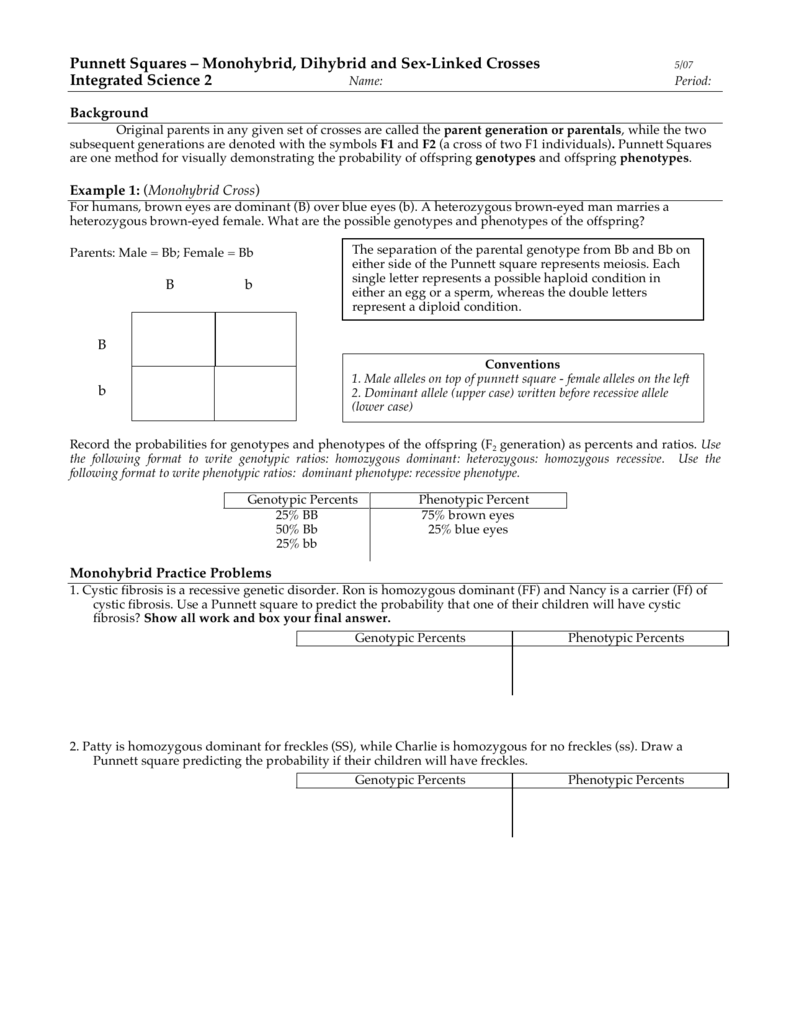
F1 Generation Punnett Square : What Are The Genotype And Phenotype Ratios Of The F2 Generation Of A Snapdragon Exhibiting Incomplete Dominance For Red And White Flowers Quora / Below is a sampling of punnett square problems that you will be expected to solve.
F1 Generation Punnett Square : What Are The Genotype And Phenotype Ratios Of The F2 Generation Of A Snapdragon Exhibiting Incomplete Dominance For Red And White Flowers Quora / Below is a sampling of punnett square problems that you will be expected to solve.. To draw a square, write all possible allele * combinations one parent can contribute to its gametes across the top of a box and. It turned out that the f1 generation consisted of all violet flowers, so he called the violet trait dominant, while the white trait which appeared to be lost in the. When a punnett square will not be useful. The f2 generation was created by selfing the f1 plants. The punnett square is used to show how the genes of parents (the genes of which are already known) might combine in their offspring.
Punnett squares answer key directions: Punnett, who devised the approach. The f2 generation was created by selfing the f1 plants. Draw a punnett square for this generation and determine the phenotypic ratio. A punnett square simulates two organisms reproducing sexually, examining just one of the many genes that get passed on.
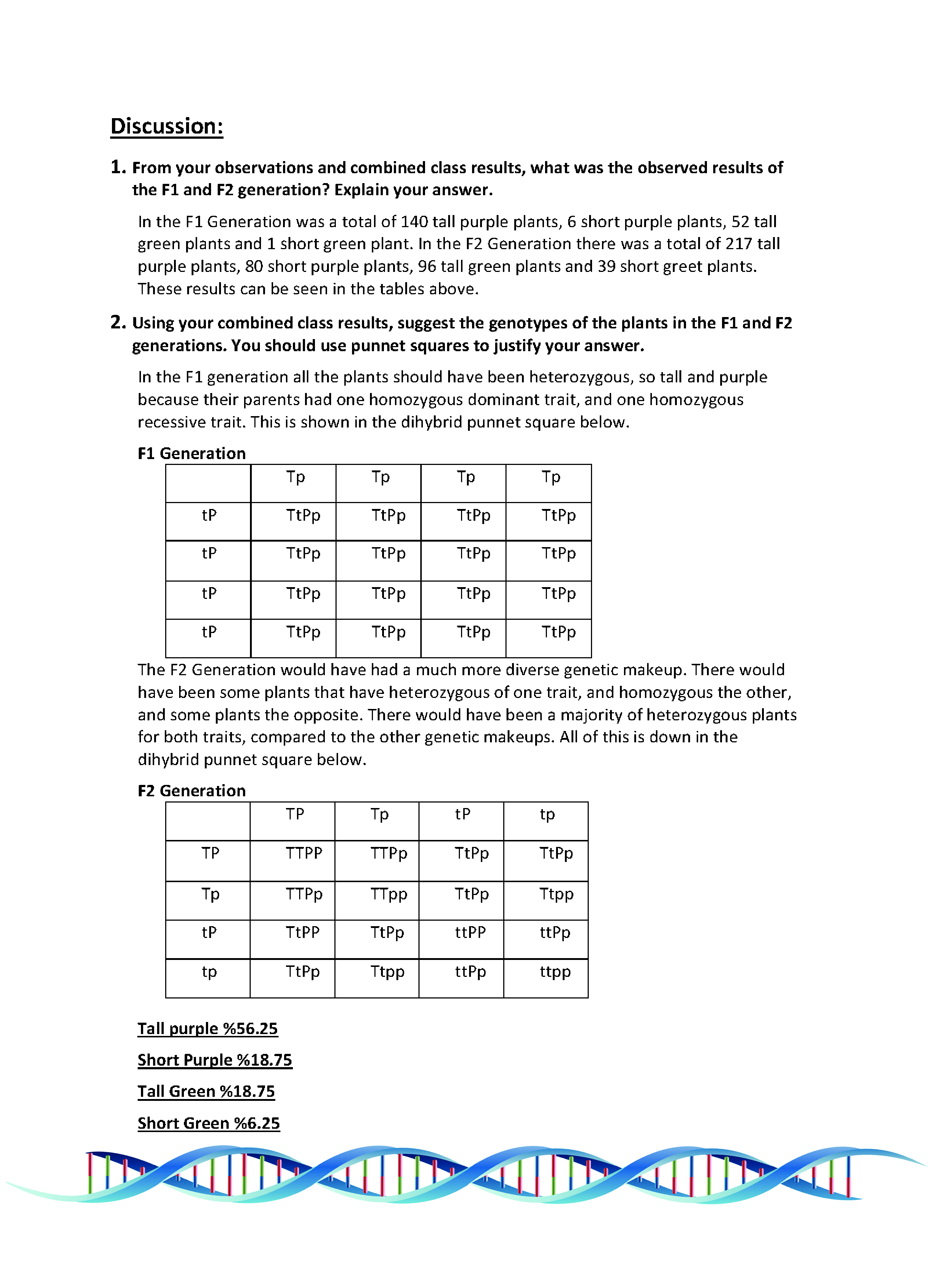
O homozygous dominant = o heterozygous = o homozygous recessive =.
This video uses a punnett square to illustrate now let's cross the f1 flowers to create the second filial, or f2, generation. 15 genetic drift in each generation, some individuals may, just by chance, leave behind a few more descendents (and genes, of course!) than other individuals. A a a aa aa a aa aa aa = pink b. A punnett square shows the probability of an offspring with a given genotype resulting from a cross. Below is a sampling of punnett square problems that you will be expected to solve. This means that f1 generation is heterozygous, but the phenotype is the dominant brown eyes gene. Punnett squares are a useful tool for predicting what the offspring will look like when mating plants or animals. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. The completed square shows every possible way the offspring could inherit this gene, and what the chances are for each result. The genes of the next generation will be the genes of the lucky individuals, not necessarily the healthier or better individuals. Reginald crundall punnett, a mathematician now we see how it was possible for the green pea phenotype to skip a generation. O homozygous dominant = o heterozygous = o homozygous recessive =. It is a simple box of four squares.
To draw a square, write all possible allele * combinations one parent can contribute to its gametes across the top of a box and. Work the following problems out in your notebook or on a separate piece of paper. The genes of the next generation will be the genes of the lucky individuals, not necessarily the healthier or better individuals. The f2 generation was created by selfing the f1 plants. Punnett squares are a grid method of organizing and understanding simple genetic information and the possible genotypic outcome of progeny.
Punnett squares answer key directions:
The green pea allele was present in the f1 generation, but the. First the punnett square is shown. You need to predict the phenotypic ratios of the f 1 and f 2 generations of a cross between true breeding individuals for a trait that exhibits incomplete dominance. What a punnett square does is that it tells you, given the genotypes of the parents, what alleles are likely to be expressed in the offspring. Their offspring will get one allele of the y gene and one allele of the r gene from each parent. A punnett square shows the genotypes two individuals can produce when crossed. From these results mendel coined several other terms and formulated his first law. As far as i remember, punnet square is not drawn to decide which type of gametes will be formed, but it is drawn, when the gametes are crossed to produce f1, f2 etc generations to check the genotypes. The first generation of offspring from p generation (means first filial: Punnett squares are helpful much of the time, even when comparing multiple traits or ones with complex dominance all of the plants in the f1 generation had round seeds. Use the punnett square to track dominant and recessive allele pairings that make up a trait's genotype. Lists all possible gamete combinations from a cross and figures out all possible genotypes from a cross. Punnett squares are a grid method of organizing and understanding simple genetic information and the possible genotypic outcome of progeny.
The classic example of this would be mendel's peas. Below is a sampling of punnett square problems that you will be expected to solve. A punnett square is just a tool or method to help you to make a cross when parents produce different gametes. This video uses a punnett square to illustrate now let's cross the f1 flowers to create the second filial, or f2, generation. This can be depicted graphically in a punnett square.

For example, if he crossed two plants both heterozygous for height, where t figure caption:
Punnett, who devised the approach. From these results mendel coined several other terms and formulated his first law. P generation _ generation 2. This video uses a punnett square to illustrate now let's cross the f1 flowers to create the second filial, or f2, generation. What a punnett square does is that it tells you, given the genotypes of the parents, what alleles are likely to be expressed in the offspring. Draw a punnett square for this generation and determine the phenotypic ratio. Suppose you have a parent plant with purple flowers identify the ratios of traits that mendel observed in the f2 generation. Draw a punnett square and cross two of the heterozygous offspring from the f1 generation. The classic example of this would be mendel's peas. Punnett squares are helpful much of the time, even when comparing multiple traits or ones with complex dominance all of the plants in the f1 generation had round seeds. Punnett squares • monohybrid example in guinea pigs, black coat is dominant to white coat. A punnett square shows the genotypes two individuals can produce when crossed. Use aa for red and aa for white.
Komentar
Posting Komentar